✔ 100% Authentic Product
👁️ Currently Viewing 3060
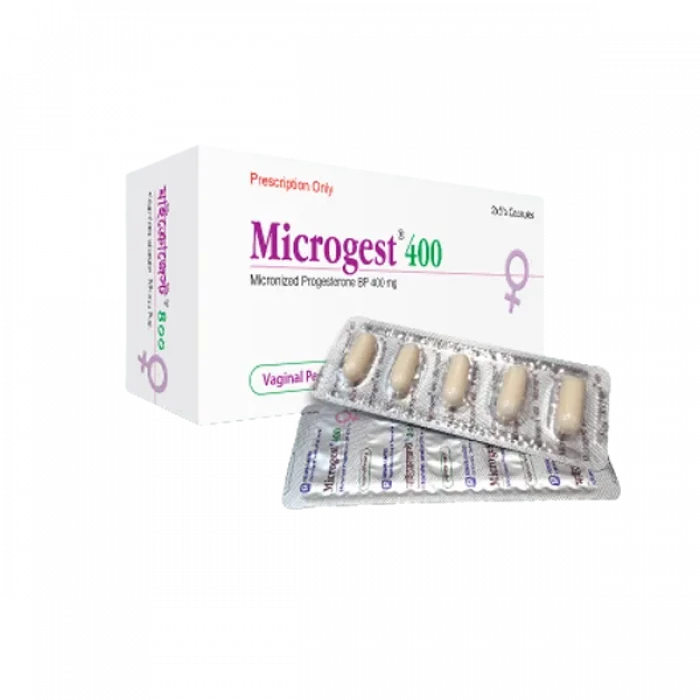
Microgest 400 Vaginal Pessary 5pcs
Generic Name: Progesterone (Vaginal Pessary) 400mg
Company Name: Renata Pharma Ltd
Discount
Price: ৳ 245
MRP:
৳
250
2%
Off

100% Genuine Products, Guaranteed

Safe & Secure Payments, Always

Fast, Secure & Efficient Delivery

Proper Packaging
 Cash on Delivery - All over Bangladesh
Cash on Delivery - All over Bangladesh Regular Delivery - 12-24 Hours, Dhaka City* Charge Tk.39-59
Regular Delivery - 12-24 Hours, Dhaka City* Charge Tk.39-59 Regular Delivery - 24-48 Hours, Other Cities* Charge Tk.99-110
Regular Delivery - 24-48 Hours, Other Cities* Charge Tk.99-110
 ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকা
শহরে
ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকা
শহরে ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ২৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকার
বাহিরে
ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ২৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকার
বাহিরে
100% Genuine Products, Guaranteed
Safe & Secure Payments, Always
Fast, Secure & Efficient Delivery
Proper Packaging
 Cash on Delivery - All over Bangladesh
Cash on Delivery - All over Bangladesh Regular Delivery - 12-24 Hours, Dhaka City* Charge Tk.39-59
Regular Delivery - 12-24 Hours, Dhaka City* Charge Tk.39-59 Regular Delivery - 24-48 Hours, Other Cities* Charge Tk.99-110
Regular Delivery - 24-48 Hours, Other Cities* Charge Tk.99-110 ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকা
শহরে
ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকা
শহরে ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ২৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকার
বাহিরে
ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ২৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকার
বাহিরে
✅ Description:
Indications
Progesterone, a female sex hormone, is present in Microgest 400 Vaginal Pessary. It is used to address problems with menstruation and pregnancy brought on by hormonal imbalance. In order to avoid endometrial hyperplasia, it is also recommended in conjunction with estrogen as part of hormone replacement therapy (thickening of the lining of the uterus).
- Micronized progesterone is used to support the luteal phase in women who are undergoing Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART).
- Premenstrual syndrome, including premenstrual tension and sadness, is treated.
- Puerperal depression is treated.
Pharmacology
Natural endogenous progesterone is physically and physiologically similar to Micronized Progesterone Vaginal Pessary.
Absorption: In healthy women, vaginal administration of 400 mg progesterone every 12 hours has been demonstrated to be successful in swiftly attaining and maintaining serum progesterone concentrations at physiological levels adequate for the ovarian cycle's mid-luteal phase and early pregnancy.
Progesterone is predominantly attached to serum albumin and corticosteroid-binding globulin, with around 96 percent to 99 percent associated with serum proteins.
Progesterone is predominantly processed by the liver, which produces pregnanediol and pregnanolones. Pregnanediols and pregnanolones are converted to glucuronide and sulfate metabolites in the liver. Bile-excreted progesterone metabolites can be deconjugated and subsequently metabolized in the gut through reduction, dehydroxylation, and epimerization.
Progesterone is eliminated by the kidneys and bile ducts.
Dosage & Administration
For luteal phase support as part of an ART treatment: 400 mg was administered vaginally twice a day starting at oocyte retrieval. The administration of Progesterone should be continued for 38 days if pregnancy has been confirmed.
For maintenance of Pregnancy in cases of Threatened or recurrent abortion: 200 to 400 mg per day in divided doses.
For the treatment of premenstrual syndrome and puerperal depression: 200 mg daily to 400mg twice a day, by vaginal or rectal insertion. For premenstrual syndrome commence treatment on day 14 of the menstrual cycle and continue treatment until the onset of menstruation. If symptoms are present at ovulation commence treatment on day 12.
Interaction
Rifampicin, carbamazepine, and phenytoin are examples of drugs that stimulate the hepatic cytochrome-P450-3A4 system, which can increase the clearance rate and hence decrease progesterone bioavailability. Concomitant vaginal products have not been studied for their effect on progesterone exposure from Micronized Progesterone, thus they are not suggested.
Contraindications
- Hypersensitivity to the active ingredient or any of the excipients is a serious condition.
- Vaginal bleeding that hasn't been diagnosed
- Progesterone-sensitive malignant tumors that are known or suspected Porphyria
- Hepatic illness or severe hepatic dysfunction
- Missed abortions or ectopic pregnancies that have been documented
- History of arterial or venous thromboembolism, severe thrombophlebitis, or active arterial or venous thromboembolism
Side Effect
The estrogenic, androgenic, and mineralocorticoid actions of micronized progesterone are absent. Mild somnolence has been recorded, as well as other CNS adverse effects such as depression, breast discomfort, and bloating. When using the vaginal method, there are fewer side effects.
Pregnancy & Lactation
Progesterone is known as the “pregnancy hormone.”
Progesterone helps the fertilized egg be implanted in the uterus to establish a pregnancy and help maintain a healthy pregnancy.
Women naturally produce progesterone in the ovaries, the placenta, and the adrenal glands during pregnancy.
During fertility treatments such as IVF (in vitro fertilization), progesterone is often given because the medications used in the process reduce a woman’s natural production of the hormone.
Precautions & Warnings
In the case of a threatening miscarriage, micronized progesterone is not recommended. In the event of a missed miscarriage, treatment should be stopped. If any of the following problems are suspected, micronized progesterone should be stopped: Myocardial infarction, cerebrovascular problems, arterial or venous thromboembolism (pulmonary embolism or venous thromboembolism), thrombophlebitis, or retinal thrombosis are all examples of thromboembolism.
Storage Conditions
Keep the container cold (below 30°C), dry, and dark. Keep out of children's reach.
⚠️Disclaimer:
At ePharma, we’re committed to providing accurate and accessible health information. However, all content is intended for informational purposes only and should not replace medical advice from a qualified physician. Please consult your healthcare provider for personalized guidance. We aim to support, not substitute, the doctor-patient relationship.